It’s a long-standing cliche: forewarned is forearmed.
But cliches exist for a reason because they have become proven in practical examples time and time again.
That’s why in this technological age that evolves by the second, the ability to anticipate and prevent emergencies before they occur has become a critical competitive advantage for building owners.
While traditional reactive approaches to emergency management focus on responding after incidents happen, forward-thinking organizations are embracing smart building technology to identify risks, prevent crises, and protect their most valuable assets—their people, property, and brand reputation.
What is Smart Building Technology and Why It Matters for Emergency Prevention
Smart building technology represents a fundamental shift in how businesses approach safety and emergency preparedness. By leveraging interconnected systems—environmental sensors, intelligent monitoring platforms, automated building controls, and data analytics—organizations can identify potential risks before they manifest into actual emergencies. This proactive approach enables businesses to implement targeted interventions, optimize resource allocation, and create more resilient operational environments.
Organizations implementing smart building technology for emergency risk management see an average reduction of 40-60% in incident-related costs, significantly improved regulatory compliance, and enhanced employee safety outcomes compared to traditional reactive approaches.
Smart building technology companies are at the forefront of this transformation, developing sophisticated platforms that integrate various data streams to create comprehensive emergency prevention systems.
These solutions go far beyond simple monitoring to provide intelligent insights that help facility managers, security teams, and executives make informed decisions about risk mitigation and resource allocation.
It’s all about finding emergency management software to bridge the gap between chaos and coordination.

Smart Building Technology Advancements in Emergency Risk Management
The Evolution from Reactive to Predictive Systems
For decades, businesses have operated under a reactive emergency management model: incidents occur, teams respond, damage is assessed, and lessons are learned for next time.
However, this approach carries significant costs—not just in terms of property damage and business interruption, but also in legal liability, regulatory compliance issues, and brand reputation damage that can take years to recover from.
Smart building technology advancements have fundamentally changed this paradigm.
Modern systems can process vast amounts of data from multiple sources—environmental sensors, historical incident patterns, building systems, and operational metrics—to identify potential risks before they manifest into actual emergencies.
Comprehensive Data Integration and Intelligence
The foundation of effective smart building technology lies in comprehensive data collection across multiple domains. Modern emergency management platforms integrate various data streams to create a holistic view of organizational risk.
Environmental monitoring systems continuously track temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, air quality metrics, and other conditions that could indicate developing problems.
Building systems data provides crucial insights into HVAC performance, electrical load patterns, fire safety system status, and structural monitoring metrics.
Operational data adds another layer, including employee movement patterns, equipment utilization rates, maintenance schedules, and workflow disruptions.
Historical incident data provides the baseline for pattern recognition, enabling systems to identify recurring risk factors and seasonal variations in emergency types and frequencies.
Smart Building Technology Examples in Action
Pattern Recognition and Automated Risk Identification
Advanced building technology examples demonstrate how artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can process multi-dimensional data to identify subtle patterns that human observers might miss.
These systems can detect anomalies in system performance that precede equipment failures, recognize environmental conditions that historically correlate with safety incidents, and identify operational patterns that increase vulnerability to various emergency types.
For example, one system might identify that a specific combination of high humidity, elevated electrical loads, and delayed maintenance schedules has historically preceded electrical system failures.
By recognizing these patterns early, facility managers can implement preventive maintenance, adjust operational parameters, or relocate critical operations before problems occur.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Alerts
Other examples include sophisticated environmental monitoring systems that go beyond simple threshold alerts. Rather than only triggering alarms when conditions exceed predetermined limits, intelligent systems identify trending patterns that suggest future problems.
Gradually increasing temperature trends in server rooms and data centers might not trigger traditional alarms until critical thresholds are reached, but smart building technology can identify these trends early and recommend proactive measures.
Leading Smart Building Technology Companies and Solutions
BSS: Pioneering Smart Building Technology for Emergency Prevention
Building Safety Solutions (BSS) exemplifies how companies are developing comprehensive solutions for proactive emergency management.
Their approach combines real-time monitoring, intelligent analytics, and actionable response capabilities to create integrated safety ecosystems that prevent incidents rather than simply respond to them.
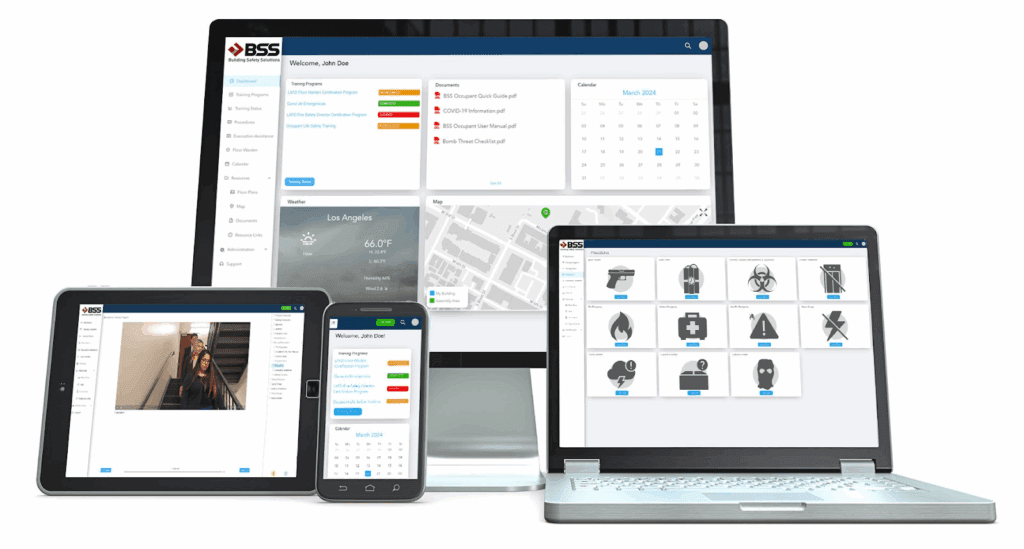
BSS Guardian and BSS First Responder: Advanced Smart Building Technology Platforms
BSS Guardian and BSS First Responder represent a prime smart building technology example of comprehensive emergency preparedness and incident management systems. As the Internet of Things (IOTs) and its related integration continue to evolve in buildings, these platforms that operate 24/7 across all devices, will be able to provide continuous monitoring and intelligent analysis capabilities. The systems will integrate multiple data sources to create predictive risk models specific to each facility and operational environment.
In the case of BSS First Responder, its communication capabilities will enable rapid coordination of preventive measures when the system identifies elevated risk conditions, helping teams implement targeted interventions before incidents occur.
The capabilities of these products extend beyond simple monitoring to include intelligent forecasting of potential emergency scenarios.
By analyzing historical patterns, current conditions, and external factors such as weather data and local threat intelligence, BSS Guardian and BSS First Responder will generate dynamic risk probability assessments. This enables organizations to adjust staffing levels, modify operational procedures, and implement preventive measures based on continuously changing risk profiles—a perfect example of how emergency management
Smart Building Technology Advancements: Implementation Strategies
Systematic Risk Assessment and Pattern Documentation
Organizations should implement regular, systematic risk assessments that leverage smart building technology to identify facility-specific vulnerabilities and operational patterns. This includes documenting seasonal variations in risk factors, analyzing relationships between operational changes and incident rates, and identifying environmental or operational conditions that consistently precede problems.
Effective risk assessment involves collaboration between multiple departments—facilities management, operations, human resources, and security—to create comprehensive risk profiles. Each department contributes unique insights that, when integrated through smart building technology platforms, provide complete visibility into potential vulnerabilities.
Proactive Maintenance and System Optimization
Predictive maintenance systems represent one of the most practical applications in emergency prevention.
Rather than waiting for equipment failures or following rigid maintenance schedules, organizations can use data-driven approaches enabled by smart building technology to optimize maintenance timing and resource allocation.
This methodology involves tracking equipment performance metrics, correlating maintenance activities with system reliability, and identifying optimal maintenance intervals based on actual usage patterns.
When combined with environmental monitoring, organizations can identify conditions that accelerate equipment degradation and adjust maintenance schedules accordingly.
Cultural Integration and Training Programs
Smart building technology examples are only effective when integrated into organizational culture through comprehensive training and awareness programs. Employees at all levels should understand how to interact with emergency management tools and recognize how their observations contribute to predictive intelligence.
Training programs should emphasize how the technology features of the software protect employees and enable them to become active participants in risk prevention rather than passive recipients of safety protocols.
When employees understand how their input enhances smart building technology systems, they contribute more effectively to overall safety outcomes.
Smart Building Technology Companies: Choosing the Right Partner
Phased Technology Deployment
Organizations implementing incident response systems for emergency management should consider partnering with building safety companies that support phased approaches. Initial phases might focus on basic environmental monitoring and historical data analysis, while advanced phases incorporate machine learning algorithms and automated response systems.
This phased approach allows organizations to develop internal expertise with these strategies, refine processes, and demonstrate value before making larger technology investments. It also ensures that human factors keep pace with building technology advancements.

What is Smart Building Technology’s Future in Emergency Management?
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The next generation of smart building technology will incorporate more sophisticated artificial intelligence capabilities, enabling more accurate predictions and automated response systems.
Many companies are developing machine learning algorithms that continuously improve their ability to identify complex patterns and correlate seemingly unrelated variables.
These advanced systems will process unstructured data sources—such as social media feeds, news reports, and weather forecasts—alongside traditional operational data to create more comprehensive risk assessments.
Natural language processing capabilities will enable smart technology to analyze incident reports, maintenance logs, and other text-based information sources for predictive insights.
Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion
Technological advancements will continue expanding with IoT device integration, providing unprecedented visibility into operational conditions and potential risk factors.
Smart sensors, connected equipment, and mobile devices will generate vast amounts of data that can be analyzed through smart building technology platforms for predictive insights.
However, this expansion requires sophisticated smart building technology companies capable of processing and analyzing massive data volumes in real-time.
Measuring Success
Quantifying Risk Reduction
Organizations implementing smart building technology for emergency management should establish baseline measurements for incident frequency, severity, and associated costs.
Success metrics should include reductions in emergency response costs, decreased business interruption time, lower insurance claims, and improved regulatory compliance scores.
More sophisticated measurements might include leading indicators such as the number of potential incidents prevented, reduction in high-risk conditions identified by monitoring systems, and improvements in system reliability metrics.
These proactive measures demonstrate the value of smart building technology approaches even when dramatic incidents don’t occur.
Legal Liability Management and Compliance Benefits
This same technology provides substantial benefits for legal liability management and regulatory compliance. By demonstrating proactive risk management efforts through smart building technology systems, organizations can reduce exposure to negligence claims and regulatory penalties.
Organizations that can demonstrate systematic, data-driven emergency preparedness often receive favorable consideration in regulatory reviews and may qualify for reduced insurance premiums.
Building Resilient Organizations Through Smart Building Technology
The transformation from reactive to predictive emergency management represents more than a technological upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift in how organizations approach risk, safety, and operational resilience.
By leveraging sophisticated platforms offered by leading smart building technology companies like Building Safety Solutions, combined with sound methodological approaches and organizational commitment, businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability to emergencies while protecting their most valuable assets.
Understanding what is smart building technology, and how it transforms emergency management is crucial for modern organizations.
Smart building technology is not simply about deploying advanced systems, but about creating comprehensive frameworks that integrate data, technology, human expertise, and organizational culture into cohesive risk management strategies.
The key to success lies in selecting the right smart building technology companies and implementing systems that align with organizational needs and capabilities. When you do, these technological advancements will provide new opportunities for enhanced safety, reduced costs, and improved operational efficiency.
The future belongs to organizations that can leverage smart building technology to see around corners, anticipate challenges before they become crises, and turn risk management from a cost center into a competitive advantage.
About Building Safety Solutions
Building Safety Solutions, Inc. (BSS) is the worldwide leader in providing emergency preparedness software, disaster management technology, and rapid response software. By protecting the life of your business, our proprietary technology limits legal liability exposure, secures your brand and saves the lives of your employees.
Contact us today for more information and a free consultation to learn how to protect your business today and tomorrow.

